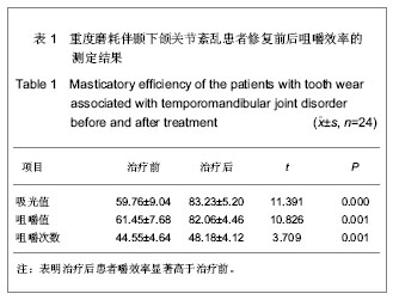
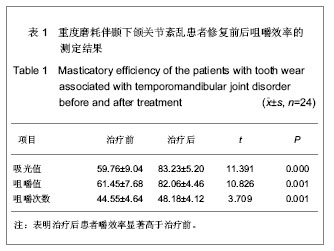
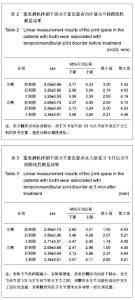
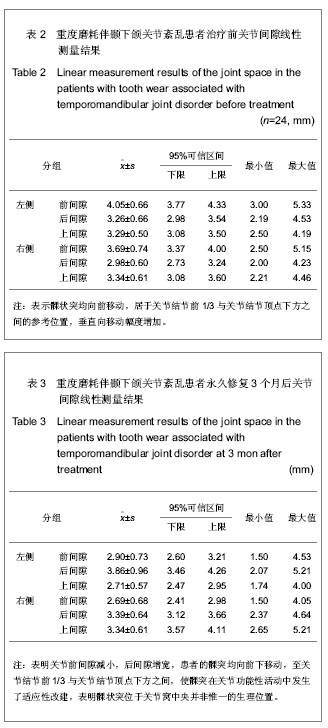
| [1] Ma XX.Beijing: Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House. 2003:453.马轩祥.口腔修复学[M].5版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2003:453.[2] Pi T.Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House. 2003: 257-258.皮听.口腔解剖生理学[M]. 5版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2003 257-258.[3] Xu JW.Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House. 1999; 666- 669.徐君伍.口腔修复理论与临床[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1999; 666- 669.[4] He MY,Nie LP,He MD,et al.Kouqiang Hemian Xiufuxue Zazhi. 2002;3(4): 232-234.何明宜,聂丽萍,何明弟,等.牙合垫式可摘局部义齿修复TMD患者牙列缺损的探[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2002, 3(4): 232- 234.[5] Zhang ZK,Zhao FY,Sun FY.Zhonghua Yixue Zazhi. 1975 ; 2 : 130.张震康,赵福运,孙广熙.正常成人颞颌关节100例X射线分析[J].中华医学杂志,1975,2 : 130.[6] Ronquillo HI, Guay J, Tallents RH, et al. Compar ison of internal derangements with condyle- fossa relationships,hor izontal and ver tical over lap, and Angle Class. JCraniomandib Disord.1988;2(3):137-140.[7] Song ZJ,Lin L,Yang PY,et al.Kouqiang Yixue.1988;8 (1):70.宋兆峻,林丽,杨宠莹,等. 用吸光度法测定咀嚼效能的研究[J]. 口腔医学,1988,8(1):70.[8] An J,Guo XM.Zhongwai Yiliao.2012;31(17):59.安涓,郭晓梅.重建治疗重度磨损引起的食物嵌塞和TMD20例分析[J].中外医疗,2012,31(17):59.[9] Liu XH,Yang XB.Baotou Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2012;28(2): 64-66.刘学慧,杨新波.可摘局部义齿及固定修复对重度磨耗或伴牙列缺损的咬合重建临床分析[J]. 包头医学院学报, 2012,28(2): 64-66.[10] Guo WB.Dangdai Yixue. 2011:17(8):51.郭卫兵.咬合重建修复重度磨耗伴牙列缺损20例疗效分析[J]. 当代医学,2011,17(8):51.[11] Yuan LJ,Fang B.Zhongguo Kouqiang Hemian Waike Zazhi. 2011;9(4):327-333.袁玲君,房兵. 骨性Ⅱ类错牙合伴颞下颌关节紊乱矫正后的长期稳定性[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,9(4):327-333. [12] Hoyt DF, Wickler SJ, Biewener AA, et al. In vivo musclefunction vs speed. I. Muscle strain in relation to lengthchange of the muscle- tendon unit.J Exp Biol. 2005;208(Pt 6): 1175-1190.[13] Hemmings KW,Darbar UR,Vaughan S.Tooth wear treatedwith direct composite restorations at an increased ver tical dimension: results at 30 months. J Prosthet Dent.2000;83(3): 287-293. |